CAI Test: Compression After Impact
The compression after impact test is a test method used to determine the compressive residual strength of a laminate material after damage has been caused by impact. The CAI test is used to draw conclusions about the damage tolerance of a multilayer composite.
The ASTM D7136 and ASTM D7137 standards describe the pre-damaging process using a drop weight tester, or the compression test for measurement of the damage resistance of composites. The CAI test is also described in standards including ISO 18352, Airbus AITM1-0010 and Boeing BSS 7260 type II.
CAI test objective Standards Pre-damaging the test plates CAI compression test Downloads
Objective of the compression after impact test
The compression after impact (CAI) test is used to determine the compressive residual strength of a laminate material after damage has been caused by impact. The specimen made of a multidirectional laminate is first pre-damaged with an impact energy specified in the respective test standard.
Using impact testing and the determination of the compressive residual strength from the subsequent static compression test, the damage resistance of a fiber composite laminate to possible impact damage can be evaluated. For composite structures used in aviation, impact damage can be caused, for example, by tool drop during maintenance, rockfall during takeoff and landing or collision with ground support vehicles.
Since the damage on the impact side is often difficult to detect, it is often referred to as “barely visible impact damage,” while inside the laminate and on the opposite side, some massive damage with significant matrix cracks and delaminations can occur.
Here, the CAI test can be divided into three phases:
- The application of impact damage using a suitable drop weight tester and the impact energy specified in the used standard.
- Evaluation and documentation of the impact damage by measuring the deformation on the impact location and additional evaluation of the damage inside the laminate through the use of a non-destructive test method, e.g. via ultrasound (C-scan).
Note: The non-destructive test (NDT) via C-scan is not part of the ZwickRoell portfolio. For this we refer to third-party suppliers. - Determination of the static compressive residual strength by using a suitable static materials testing machine and CAI test fixture.
Which standards are used when performing CAI tests?
Commonly used standards for the compression after impact test include
- ASTM D7136: Measuring the Damage Resistance of a Fiber-Reinforced Polymer Matrix Composite to a Drop-Weight Impact Event
- ASTM D7137: Compressive Residual Strength Properties of Damaged Polymer Matrix Composite Plates
- ISO 18352: Determination of Compression-After-Impact Properties at a Specified Impact-Energy Level
- AITM1-0010: Airbus Test Method for Determination of Compression Strength After Impact
- Boeing BSS 7260, Type II: Post-Impact Compressive Strength Test on Composite Laminates
The ASTM D7136 standard describes the impact test and the evaluation and documentation of the impact damage after the test. ASTM D7137 describes the static compression test for determination of the compressive residual strength of the damaged laminate.
All other standards mentioned above describe the three phases of the test performance, although the procedure for determination of the inside damage via non-destructive testing is not described in detail.
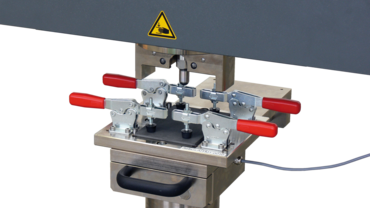
Performing the CAI test: pre-damaging the specimen
In the HIT230F or HIT600F instrumented drop weight tester, the specimen is pre-damaged using a clamping fixture and impact energy specified in one of the standards. Depending on the standard used, the dimensions of the clamping device and the clamping position may differ slightly.
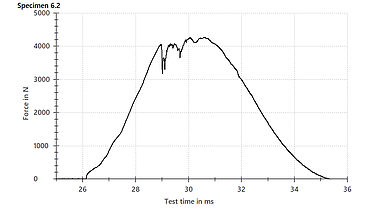
For easier testing, the specimens are gripped outside of the drop weight tester and then moved into testing position. For the impact test, it is important to use a drop weight tester with an anti-rebound system, to avoid masking the initial impact damage through repeated impact of the specimen with the impactor. Using an instrumented drop weight tester also makes is easy to determine the force curve, the impact velocity and the impact energy absorbed by the specimen.
Related testing machines for pre-damaging test plates
The HIT230F instrumented drop weight tester with an adjustable drop height up to 1 meter, integrated speed measurement on the point of impact, anti-rebound device, corresponding impactor for the impact test (16 mm diameter) and the easily changeable weights for setting different impact energies is specifically designed to meet the requirements for pre-damaging CAI specimens.
The HIT600F instrumented drop weight tester is also ideal for the application of pre-damaging forces in the CAI test, and can reach even higher velocities and impact energies with a higher drop distance setting and the addition of an optional acceleration unit. It is therefore also suitable for the performance of multi-axial puncture tests on plastic specimens.
Performing the CAI test: static compression test
After pre-damaging the specimen in the impact test on the drop weight tester and the evaluation of the impact damage by measuring the deformation on the impact location and determination of the extent of damage on the inside of the laminate through non-destructive testing, the actual static compression test for determination of the CAI compressive residual strength can be implemented.
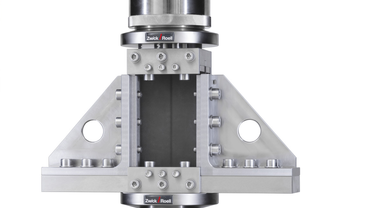
For this test, the pre-damaged specimen is installed in a special CAI compression test fixture. Since the general requirements for specimen clamping differ in the CAI test standards, two different compression test fixtures are used.
- For ASTM D7137 and Boeing BSS 7260 Type II, the specimen is guided on all four sides, but not gripped
- For ISO 18352 and Airbus AITM1-0010, the specimen is gripped at the top and bottom and guided on the sides through line contact
CAI compression test fixture (compression after impact)
The CAI fixture is positioned between two compression platens in the static materials testing machine. During the CAI test, the specimen is subjected to a compressive load up to the point of failure. The compression after impact test is valid if the specimen fails in the area of the centrally applied impact damage. Failure at or near the upper or lower clamp is not permitted.
Benefits:
- Easy specimen changes through simple handling of the CAI fixture
- Use in a large temperature range of -70 °C to +300 °C
- Increased side stiffness through support bars prevents lateral bending of the fixture, especially when using unconventional laminate structures
- Interchangeable carbide inserts on the upper and lower contact surfaces with the specimen minimize wear of the heavily loaded force application surfaces
Compression After Impact (CAI) Test to ASTM D7137
During compression after impact (CAI) tests, a pre-damaged composite specimen is tested using a special compression test fixture up to 600 kN. The compression after impact test is performed with a Z600E materials testing machine in a temperature range of -60 °C to +350 °C.
Related testing machines for the CAI compression test
In the compression after impact test, the use of a relatively large specimen measuring 100 mm x 150 mm x 5 mm (width x length x thickness) can easily generate forces in excess of 100 kN. This also depends on the type of composite material tested (e.g. CFRP or GFRP), the type of fiber reinforcement used (e.g. UD, scrim or fabric), or use of laminate constructions and laminate thicknesses other than the nominal laminate constructions and laminate thicknesses defined in the above test standards.
CAI tests should therefore be performed on a static materials testing machine with a nominal load of 150 kN to 250 kN. For the CAI test with very thick laminates, reinforced CAI fixtures and static materials testing machines with a higher nominal load up to 600 kN can also be used.
To verify accurate alignment of the test arrangement and the dimensional accuracy of the CAI compression fixture, test specimens with strain gauges applied to both sides must be used for each test when setting up the test arrangement or at specified intervals, depending on the CAI test standard used (a total of 4 per specimen). The strain gauge signals can either be integrated into the testing machine with pre-assembled strain gauge boxes or by using a suitable universal measuring amplifier.
FAQ
An impact test is used to pre-damage a composite specimen. A subsequent static compression test determines the compressive residual strength of the specimen. This allows for the evaluation of the damage resistance of a fiber composite laminate to impact damages.
Compression after impact (also CAI test) simulates damages to a composite material, such as those that can occur in aircraft or vehicles as a result of rock or bird impacts or accidents. The characteristic value determined through this test is referred to as compressive residual strength.
For the CAI test, you need a drop weight tester to pre-damage the specimen and a statice materials testing machine for the static compression test.