- HDT heat deflection temperature
- VST Vicat softening temperature
- Creep test
- ISO 75, ASTM D648
- ISO 306, ASTM D1525
- ISO 2507
- Oil bath
Applications
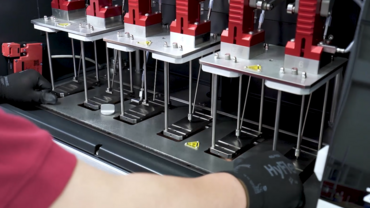
With the Amsler Allround heat deflection tester, ZwickRoell offers a motorized HDT/Vicat tester with a fully automated test sequence for determining Vicat softening and heat deflection temperatures up to 300 °C to ISO and ASTM standards:
- Determination of the heat deflection temperature (HDT) according to ISO 75 parts 1 to 3 and ASTM D648 on thermoplastics, ebonite, as well as fiber-reinforced and filled curable plastics.
- Determination of the Vicat softening temperature (VST) according to ISO 306 and ASTM D1525 on thermoplastics and according to ISO 2507 on pipes and fittings made of thermoplastics.
- Determination of creep behavior under bending stress.
The heat deflection tester is designed for convenient testing in the fields of research and development, goods inwards checks and production monitoring. Depending on requirements, the instrument can be equipped with 2, 4 or 6 test stations, allowing HDT and Vicat tests to be carried out in parallel and independently.
The Amsler Allround heat deflection tester can be operated in standalone mode with touch display or in connection with a PC. With the testXpert testing software, a meaningful analysis of the results can be realized.
Video: Heat Deflection Tester with testXpert Testing Software
The video shows the test procedure for determining the heat deflection temperature according to ISO 75 and ASTM D648 as well as the Vicat softening temperature according to ISO 306 and ASTM D1525 using the Amsler Allround heat deflection tester and our testXpert testing software.
Technical overview heat deflection tester
| Description | Value | |
| Type | Amsler Allround 6-300 heat deflection tester | |
| Item No. | 109493612 | |
| Measuring stations, default | 2 | |
| Measuring stations, possible | 6 | |
| Controllable temperature range | +20 ... +300 | °C |
| Temperature for creep test, max. | 288 | °C |
| Test time for creep test, max. | 48 | hours |
| Temperature sensor | Pt 100 | |
| 1 x per station and 1 x per bath | ||
| Heat transfer fluid holding capacity, min. | 18 | l |
| Temperature measurement | ||
| Display accuracy at 300°C | ± 0.5 | °C |
| Spatial temperature gradient | ± 0.1 | °C |
| Temperature measurement resolution | 0.01 | °C |
| Travel measurement | ||
| Measurement range | 1 ... 16 | mm |
| Displacement measurement resolution | 0.001 | mm |
| Measurement accuracy of the sensor | ± 0.002 | mm |
| Measurement accuracy of the system | ± 0.01 | mm |
| Measuring system | Linear displacement transducer (digital) | |
| Dimensions | ||
| Height, door closed | 878 | mm |
| Height, door open | 1430 | mm |
| Width | 1280 | mm |
| Depth | 700 | mm |
| Weight, with two measuring stations, without weights, without heat transfer fluid, approx. | 196 | kg |
| Required PC interface | Ethernet | |
| Cooling | Automatically or manually controlled via software | |
| Ambient temperature | +10 ... +35 | °C |
| Temperature during storage and transport | -25 ... +55 | °C |
| Relative humidity (non-condensing) | 20 ... 90 | % |
| Average noise level at vmax measured at 1 m distance from the front of the machine | <55 | dB(A) |
| Permissible height in relation to sea level for storage and operation | ≤ 2000 | m |
| Operation | Indoor | |
| Power input specifications | ||
| Power supply | 120 | V, 1Ph/N/PE |
| Permissible voltage fluctuation | ± 10 | % |
| Power consumption, max. | 30 | A |
| Power consumption (full load), approx. | 3.8 | kVA |
| Power frequency | 50/60 | Hz |
| Standards | ||
| Overvoltage category to IEC 61010-1 | II | |
| Degree of dirt and debris to IEC 61010-1 | 2 | |
- Water supply required
- The instruments are supplied without heat transfer fluid as standard. The required amount can be ordered from accessories.