Creep testing machines
Creep testing machines are used to determine the long-term strength and heat resistance of various materials. High-temperature materials, particularly those used in industries like aerospace, energy, and metals, must withstand increasingly higher loads and temperatures. Therefore, creep tests are essential for accurate and reliable material characterization.
ZwickRoell offers Kappa creep testing machines for both classic and extended creep tests, capable of operating under a wide range of environmental conditions and a broad test temperature range from -80°C to +2,000°C. Whether testing metal, ceramics, CMC, graphite, plastics or composites, Kappa systems deliver precise, reproducible and standard-compliant test results.
Creep testing machines overview High-temperature accessories up to +2,000°C Extensometer Download Request quotation / consultation
What is a creep test?
A creep test is a destructive materials testing method used to determine the long-term strength and heat resistance of a material. During the test, a specimen is subjected to a constant tensile force or tensile stress for an extended period of time, while simultaneously being subjected to increased temperature conditions. In terms of duration, a differentiation is made between short term tests up to approximately 10,000 hours and long term tests starting at approximately 10,000 hours.
The objective of a creep test is to predict the life span of a material under certain operating conditions. The testing requirements for our Kappa creep testing machines vary depending on the type of test and the temperature range.
Detailed information on long-term tests can be found here:
Test method Relevant standards for metals Relevant standards for plastics
A comparison of creep testing machines
ZwickRoell offers creep testing machines for a variety of test requirements, environmental conditions and temperature ranges.
- Lever arm testing machines (Kappa LA) are ideal for conventional long-term creep tests exceeding 10,000 hours. Force is applied via dead weight or a pretensioned spring up to a maximum test force of 50 kN.
- Electromechanical creep testing machines (Kappa DS and SS-CF) cover the entire spectrum of creep and creep applications, with test durations up to 10,000 hours and maximum test loads of 250 kN.
- Creep testing machines with multiple load axes (Kappa Multistation) feature a compact design and are ideal for running multiple simultaneous tests on a single machine.
Compare the Kappa models and find the right system for your test requirements!
| Kappa LA | Kappa DS | Kappa SS-CF | Kappa Multistation to 50 kN | Kappa Multistation to 10 kN | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
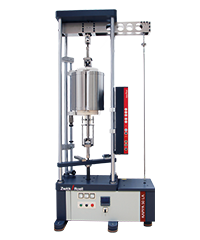 |  |  |  |  | |
| To Kappa LA | To Kappa DS | To Kappa SS-CF | To Kappa Multistation | To Kappa Multistation | |
| Material |
|
|
|
|
|
| Type of test |
|
|
|
|
|
| Max. test load | 50 kN | 250 kN* | 100 kN* | 50 kN | 10 kN |
| Number of load axes | 1 | 1 | 1 | Up to 3 | Up to 6 |
| Accessories for test temperatures from -80°C to +2,000°C | |||||
| Temperature chamber | - | • | - | - | - |
| Temperature and humidity chamber | - | - | - | • | • |
| High-temperature furnace | • | • | • | • | - |
| Induction heating | - | • | • | - | - |
| Vacuum and inert gas chambers | - | • | • | - | - |
* Higher test forces are available upon request.
“•” Installation possible, “-” Installation not possible
Video: Customized creep testing machine for tests on CMC materials up to 2,000°C
This customized Kappa testing system was developed for creep fatigue tests, as well as tensile, compression, flexure and shear tests of ceramic matrix composites (CMCs). The system enables long-term tests at extreme temperatures up to 2,000°C, under either a vacuum or inert gas atmosphere – ideal for characterizing high-temperature-resistant materials in research and industry.
Modular high-temperature accessories for creep testing machines
Accurate creep tests under defined temperature and environmental conditions is crucial for reliably determining the temperature-dependent elastic behavior, strength and yield point of high-temperature resistant materials. ZwickRoell equips creep testing machines with a wide range of modular high-temperature accessories, designed for testing in temperatures ranging from -80°C to 2,000°C.
The optimal combination of heating system, precise temperature control, suitable thermocouples, load strings and coordinated extensometers is the basis for reliable test results in creep testing.
| Temperature | Environment | Advantages | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Temperature chamber |
|
|
|
| Temperature and climatic chambers |
|
|
|
| High-temperature furnace with 1, 2 or 3 heating zones |
|
|
|
| Induction heating system |
|
|
|
| Vacuum chamber |
|
|
|
Optical extensometer
The differentiating advantage of extensometers featuring non-contact measurement is that they can be used right up to break without risk of damage, even with specimens that are critical in this respect. Especially in an elevated temperature range, non-contact extensometers provide a defining advantage over contact extensometers, since the access to different heating systems can be sealed with view windows.
Applications for the video extensometer for high temperatures:
- Long-term applications, tensile, compression and flexure tests, cyclic applications (< 2 Hz)
- A variety of materials such as metals, refractory materials, ceramics
- Temperature range: ambient temperature up to +1,400 °C
Contact extensometers
Contact extensometers for creep testing are available for tensile as well as compression and flexure tests. In addition to different accuracy classes and measurement ranges, extensometers for extended temperature ranges are also available. A distinction is made between side- and axial-attaching extensometers, which are suitable for special test types such as crack propagation testing. Depending on the specimen shape, different sensor arms are used.
Our engineers are happy to help you select the optimal system for your creep testing machine from our extensive portfolio of extensometers.

