ASTM D624 Tear Growth Test on Rubber and Elastomers
ASTM D624 describes methods for determining the tear strength or tear resistance of vulcanized rubber or thermoplastic elastomers.
The following content explains the key aspects. For standard-compliant testing in accordance with ASTM D624, however, it is essential to purchase the complete standard. Further methods for determining the tear resistance of elastomers are described in ISO 34-1/-2.
ASTM D624 is only concerned with methods for determining the tear strength of elastomers. The determination of mechanical properties of rubber in the tensile test, such as tensile stress, tensile strength and strain at break are described in ISO 37, DIN 53504 and ASTM D412.
Objectives & application Specimen Specimen preparation Running a test Testing system & accessories Automation FAQ Request a consultation
ASTM D624 objective & applications
The application of ASTM D624 ensures that tests are reproducible and comparable regardless of the respective test laboratory. The standard defines the requirements for specimen geometry, test speed, conditioning and the evaluation of the results.
The standard is applied wherever elastomers are used and mechanical stress from cracks poses a critical risk, such as in the automotive industry, rubber manufacturers or medical devices.
ASTM D624 Specimen preparation
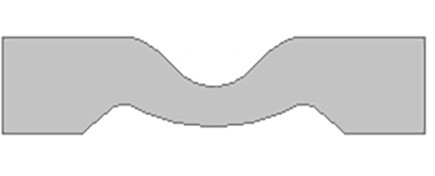
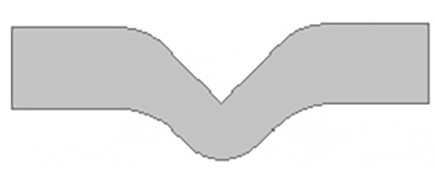
The specimens are to be punched from molded specimen plates with a thickness of 2.3 ± 1.0 mm (0.09 ± 0.04 in.), the milling direction or flow direction being clearly marked. They must be punched out with a single stroke (by hand or machine) to ensure smooth cut surfaces.
The specimens must be cut or notched to the depth specified in the standard using specified equipment.
Running a test
The specimen is inserted into the specimen grips of the testing machine in such a way that it is evenly stressed over its entire length and prevented from slipping. The machine is started and kept at a constant speed until the specimen tears completely.
For specimens type A, B or C, the recommended speed is 500 ± 50 mm/min (20 ± 2.0 in/min) and 50 ± 5 mm/min (2 ± 0.2 in/min) for type T and CP. For type A, B or C, the maximum force is determined, for type T or CP, a strip diagram or a continuous recording of the force is recorded during the entire tearing process.
ASTM D624 Testing Systems
For the test to ASTM D624, the detection of the elongation of the specimen is crucial. So that the extension can be reliably recorded until break, both the travel distance of the crosshead must be long enough and the load frame must be designed to be correspondingly high. ZwickRoell offers the right universal testing machines for this:
- zwickiLine – space-saving solution for small test loads up to 5 kN and with a test range up to 1365 mm
- ProLine - for standard-compliant tests and simple applications with a test area from 1050 mm to 1450 mm
- AllroundLine - adaptable and versatile with a test area from 1030 mm to 2560 mm
Specimen grips for tests to ASTM D624
The testing machine must be equipped with specimen grips that automatically tighten and exert uniform pressure on the gripping area while preventing the specimen from slipping. For most specimens, pneumatic grips with constant pressure are sufficient.
In the pneumatic grips from ZwickRoell, the gripping force is generated by pneumatic actuators. It can be operated with a hand or foot control. Gripping force independent of the tensile force ensures a constant test speed over the course of the entire test sequence. Screw grips or pincer grips can also be used for testing to ASTM D624.


Do you have any questions about your test requirements or challenges with ASTM D624? Please contact our experts.
They will be glad to provide the information you need!
Contact us
Automated tensile tests in accordance with ASTM D624
Tensile tests on rubber and elastomers to ASTM D624, can also be automated, meaning they can be performed with fully automatic specimen feeding. An automated testing system is primarily used when many specimens need to be tested, or when operator influences must be eliminated. Hand temperature or moisture, as well as inaccurate or angled positioning of the specimen in the specimen grips, can affect the test results.
- For large specimen series, our experts recommend the compact robotic testing systemroboTest L. It can autonomously perform tensile tests on up to 350 specimens and can be used 24/7. A thickness measuring device integrated in the system measures the specimen thickness with accuracy and reproducibility.
- The robotic testing system roboTest R is more complex and allows you to connect additional devices such as a specimen marking station or a temperature chamber for accurate tempering of the specimen.
- To avoid operator influences even with small specimen series, ZwickRoell has the testing system ALEX in its portfolio: simple, compact, and cost-effective, it can be used with a series as small as 10 specimens.
Downloads
- Product Brochure: Testing machines and testing systems for plastics and rubber PDF 9 MB
- Product Information: lightXtens: non-contact, simple, and fully automated testing of high-extension materials PDF 886 KB
- Product Information: videoXtens 1-270 P PDF 1 MB
- Product Information: multiXtens II HP extensometer PDF 1 MB
- Product Information: Robotic testing system roboTest L (linear) for plastics PDF 71 KB
- Product Information: Robotic testing system roboTest R (polar) for plastics PDF 86 KB
- Product Information: ALEX - The automated lab expert PDF 310 KB
Frequently asked questions regarding ASTM D624
The ASTM D624 standard defines methods for determining the tear resistance of vulcanized rubber and thermoplastic elastomers. Five different specimen shapes are described. During the test, the specimens are gripped and tested under tensile loading until the /specimen is torn.
ASTM D624 works with five defined specimen geometries (types A–E) and is more oriented towards US practice. ISO 34-1 offers several specimen shapes (e.g., strip, angle and crescent-shaped specimens) to represent different stress situations. ISO 34-2 describes the determination of the tear resistance of Delft specimens. The test results are not directly reproducible, as the specimens and test conditions are different.
The tear resistance according to ASTM D624 (type A, B, C) is the maximum force required to tear a specified specimen, divided by the thickness of the specimen. For type T and CP specimens, the tear resistance is the mean or median force required to produce a tear in a specimen divided by the thickness of the specimen.