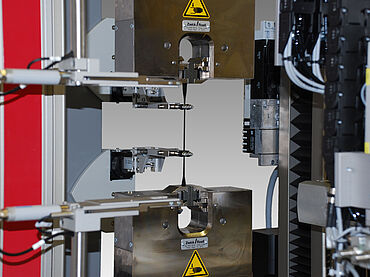
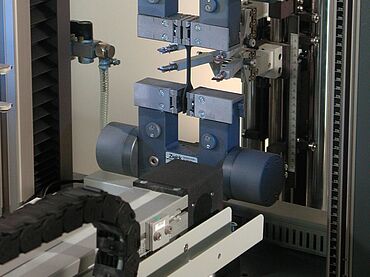
ISO 37 / DIN 53504, Tensile Test on Rubber and Elastomers
ISO 37 and DIN 53504 describe methods for determining the mechanical properties of vulcanized or thermoplastic rubber. They are designed to determine tensile stress, tensile strength and strain at break as well as the Young’s modulus values, which are defined as tensile stress at specified elongations, or vice versa. This also allows determining the yield strain and yield stress, for example, for thermoplastic elastomers. All values are determined in the tensile test at a constant pull-off speed.
Another standardized method for determining the tensile properties of vulcanized thermosetting rubber and thermoplastic elastomers is described in the standard ASTM D412.
The following content explains the key aspects. For standard-compliant testing to ISO 37 and DIN 53504, however, it is essential to purchase the complete standard.
Objectives & application Specimen Running a test Video Characteristic values Testing system Automation FAQ Request a consultation
ISO 37 / DIN 53504 Objective & applications
The use of ISO 37 / DIN 53504 ensures that tests can be run repeatable and reproducible, regardless of the testing laboratory. It defines the requirements for specimen shape, test speed, conditioning and evaluation.
The standards and tests are used along the entire value chain of the rubber industry. This starts with the raw material manufacturers and research institutions, compound development and production and also takes place in the processing industry, which manufactures products such as tires, dampers, seals, belts, conveyor belts, but also rubber gloves, condoms, or other products made of rubber.
Dumbbells to ISO 37/ DIN 53504
For the tensile test on rubber, ISO 37 and DIN 53504 specify five types of dumbbells and two permissible types of ring test specimens. The respective specimens differ only slightly between the standards.
| Type | I (min) mm | Is mm | bk mm | b mm | a mm | L0 mm | r1 mm | r2 mm | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| ISO 37 | 1 | 115 | 33±2 | 25±1 | 6.2±0.2 | 2±0.2 | 25±0.5 | 25±2 | 14±1 |
| 1A | 100 | 21±1 | 25±1 | 5±0.1 | 2±0.2 | 20±0.5 | 25±2 | 11±1 | |
| 2 | 75 | 25±1 | 12.5±1 | 4±0.1 | 2±0.2 | 20±0.5 | 12.5±1 | 8±0.5 | |
| 3 | 50 | 16±1 | 8.5±0.5 | 4±0.1 | 2±0.2 | 10±0.5 | 10±0.5 | 7.5±0.5 | |
| 4 | 35 | 12±0.5 | 6±0.5 | 2±0.1 | 1±0.1 | 10±0.5 | 3±0.1 | 3±0.1 | |
| DIN 53504 | S1 | 115 | 33 | 25 | 6 | 2±0.2 | 25 | 25 | 14 |
| S1A | 100 | 25 | 25 | 5 | 2±0.2 | 25 | 20 | 11 | |
| S2* | 75 | 25 | 12.5 | 4 | 2±0.2 | 20 | 12.5 | 8 | |
| S3 | 35 | 12 | 6 | 2 | 1±0.1 | 10 | 3 | 3 | |
| S3A | 50 | 16 | 8.5 | 4 | 2±0.2 | 10 | 10 | 7.5 |
*Note on DIN 53504: Preferably, the S2 dumbbell should be used
Ring specimens to ISO 37 / DIN 53504
| External diameter d3 | Internal diameter d4 | Width b | Thickness a | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| ISO 37* | A | 52.6 | 44.6±0.2 | 4±0.2 | 4±0.2 |
| B | 10 | 8±0.1 | 1±0.1 | 1±0.1 | |
| DIN 53504 | R1 | 52.6 | 44.6 | 4.0 | 4±0.2 or 6.3±0.3 |
| R2 | 44.6 | 36.6 | 4.0 | 4±0.2 or 6.3±0.3 |
* The ring specimen type A is preferably used. Type B is used if there is not enough material available for the larger type A specimen.
Specimen preparation
- The specimens must be manufactured and measured to DIN ISO 23529
- Dumbbells and ring specimens can usually be produced by means of a cutting press with the appropriate cutting blade for the respective specimen.
ZwickRoell has two manual cutting presses for the standard-compliant manufacture of ring specimens and dumbbells.
Running a test to ISO 37 / DIN 53504
Tests on dumbbells:
- ISO 37: Before the test, the thickness of the specimen is measured in the middle and at the ends of the parallel range and the cross-section is calculated from the median value of three measurements. After the force measurement has been zeroed in the freely suspended state, the dumbbell is inserted into the specimen grips of the testing machine along the machine axis in such a way that the stress is distributed evenly over the cross-section. To start the test in a defined strain condition, it is recommended to apply a small pre-stress of 0.1 MPa and to set the extensometer in this state.
- DIN 53504: Before the tensile test, the thickness of the dumbbell is measured at least three points at RT, preferably at the ends of the parallel area and in the middle. The initial cross-section is calculated from the median of the thickness and the blanking dimension of the specimen width of the cutting press. The dumbbell is clamped in the grips in such a way that its longitudinal axis coincides with the mechanical axis of the tensile testing machine and the specimen is held evenly without slipping. The pre-stress of about <0.1 MPa with a feed rate of <50 mm/min is started and the machine is stopped. The extensometer is attached and the machine is started at the test speed specified in the standard. The force and the change in length are recorded and displayed as a stress-strain curve. A non-contact optical measuring system is preferred for strain measurement.</li>
Test speeds:
| ISO 37 | DIN 53504 | |
|---|---|---|
| Type 1 / S1 | 500 mm/min | 500 mm/min |
| Type 1A / S1A | 500 mm/min | 500 mm/min |
| Type 2 / S2 | 500 mm/min | 200 mm/min (500 ± 50 mm/min is possible, if agreed) |
| Type 3 / S3 | 200 mm/min | 200 mm/min |
| Type 4 / S3A | 200 mm/min | 200 mm/min |
Testing with ring specimen:
- ISO 37: Before testing to ISO 37, the radial width and axial thickness are measured at six approximately evenly distributed points around the ring. The median value of each measurement series is used to calculate the cross-sectional area. Before the start of the test, the force measurement chain is zeroed in the unloaded state and the roller distance is set to the dimension specified in the standard. The specimen is placed on the rollers and the machine is started at the specified test speed. While the test is run at the test speed specified in the standard, it is important that the rollers rotate to avoid strain obstruction due to friction between the specimen and the roller.
- DIN 53504: Before the tensile test, the thickness of the specimen is measured at least three points at RT. During the tensile test on ring specimens, the change in the center distance of the rollers is used as the crosshead travel of the testing machine (see table below) for the strain measurement.
Specified roller distance:
| Rollers for | ISO 37 | DIN 53504 |
|---|---|---|
| Type A (standard) | 30 +0.2 / 0 mm | |
| Type A (alternative) | 35 +0.2 / 0 mm | |
| Type B (standard) | 5.5 +0.2 / 0 mm | |
| R1 | 35 mm | |
| R2 | 28.7 mm |
Designation of the characteristic values to DIN 53504
Tests with dumbbells or ring specimens:
- σmax = tensile strength
- σR = tear strength
- εR = strain at break
- σ50 = force at travel preselection x1%
- σ100 = force at travel preselection x2%
Additional results:
- σ200 = force at travel preselection x3%
- σ300 = force at travel preselection x5%
- σ500 = force at travel preselection x10%
ISO 37 / DIN 53504 Testing systems
A requirement of the test to ISO 37 / DIN 53504, is the elongation of the specimen. With the increasing length of the specimen, the travel distance of the crosshead must be long enough—and therefore, the load frame tall enough—to accommodate the extension of the specimen up to the point of break. ZwickRoell offers the right universal testing machine for this:
- zwickiLine – space-saving solution for small test loads up to 5 kN and with a test range up to 1365 mm
- ProLine - for standard-compliant tests and simple applications with a test area from 1050 mm to 1450 mm
- AllroundLine - adaptable and versatile with a test area from 1030 mm to 2560 mm
Specimen grips for tests to ISO 37 / DIN 53504
The selection of the appropriate specimen grips takes into account both the expected number of tests per day or week, as well as the thickness and material properties of the specimen. ZwickRoell offers various types of specimen grips for this purpose, from manual mechanical grips to comfortable pneumatically controlled systems, each with suitable jaw inserts.
- Pneumatic grips: The gripping force is generated by pneumatic actuators and can be operated with a hand or foot control. Gripping force independent of the tensile force ensures a constant test speed over the course of the entire test sequence.
- Pincer grips: double actuator grip. The gripping force is increased proportionally by the pincer principle as the tensile force increases. This ensures automatic retightening for specimens prone to shrinkage.
- Forring specimens, a tool consisting of two rotatable rollers is required.
Extensometer for tests to ISO 37 / DIN 53504
When testing dumbbells to ISO 37 / DIN 53504 not only the middle part of the test specimen stretches, but also the shoulder. The standards therefore require a defined measuring accuracy of the extensometer. These requirements can be met either by sensor arm extensometer measuring directory on the specimen or by optical / non-contact extensometers. ZwickRoell offers suitable extensometers with high measurement accuracy – from cost-efficient, manual extensometers to fully automatic systems, completely without operator influence and with maximum reproducibility of test results.
Do you have any questions about your test requirements or challenges with the ISO 37 / 53504? Please contact our experts.
They will be glad to provide the information you need!
Contact us
Automated tensile tests to ISO 37 / DIN 53504
Tensile tests on rubber and elastomers to ISO 37 / DIN 53504, can also be automated, meaning they can be performed with fully automatic specimen feeding. An automated testing system is primarily used when many specimens need to be tested, or when operator influences must be eliminated. Hand temperature or moisture, as well as inaccurate or angled positioning of the specimen in the specimen grips, can affect the test results.
- The compact roboTest L robotic testing system can autonomously test up to 350 specimens. A thickness measuring device integrated into the system measures the specimen thickness accurately and consistently. The specimen gripper places the specimen in the testing machine and the tensile test according to ISO 37 / DIN 53504 is started automatically. After the test, separate disposal grippers remove the specimen remains from the specimen grips.
- The robotic testing system roboTest R is more complex and allows you to connect additional devices such as a specimen marking station, a centering station or a temperature chamber for accurate tempering of the specimen.
- To avoid operator influences even with small specimen series (type 1+2/S1+S2), ZwickRoell has the testing system ALEX in its portfolio: simple, compact, and cost-effective, it can be used with a series as small as 10 specimens.
Downloads for the rubber tensile test ISO 37 / DIN 53504
- Product Brochure: Testing machines and testing systems for plastics and rubber PDF 9 MB
- Product Information: Pneumatic Grips, Fmax 2.5 kN PDF 3 MB
- Product Information: Pincer grips, Fmax 2.5 kN PDF 348 KB
- Product Information: Grips for Ring Specimens, Fmax 2.5 kN PDF 4 MB
- Product Information: lightXtens: non-contact, simple, and fully automated testing of high-extension materials PDF 886 KB
- Product Information: videoXtens 1-270 P PDF 1 MB
- Product Information: multiXtens II HP extensometer PDF 1 MB
- Product Information: Robotic testing system roboTest L (linear) for plastics PDF 71 KB
- Product Information: Robotic testing system roboTest R (polar) for plastics PDF 86 KB
- Product Information: ALEX - The automated lab expert PDF 310 KB
- Product Information: Cutting Presses PDF 823 KB
Frequently asked questions about ISO 37 / DIN 53504
ISO 37 and DIN 53504 describe methods for determining the mechanical properties of vulcanized or thermoplastic elastomers. They describe the performance of tensile tests on standardized specimens (dumbbells and rings) and are designed to determine tensile stress, tensile strength and strain at break as well as the Young’s modulus values, which are defined as tensile stress at specified elongations, or vice versa. This also allows determining the yield strain and yield stress, for example, for thermoplastic elastomers. All values are determined in the tensile test at a constant pull-off speed.
Both standards describe the tensile test of elastomers, but differ in details. ISO 37 is internationally oriented and mainly defines dumbbells and ring specimens of types A and B with defined dimensions and test conditions. DIN 53504 is the German version, which is largely based on ISO 37, but contains additional ring types and methods that are particularly important for industrial applications.